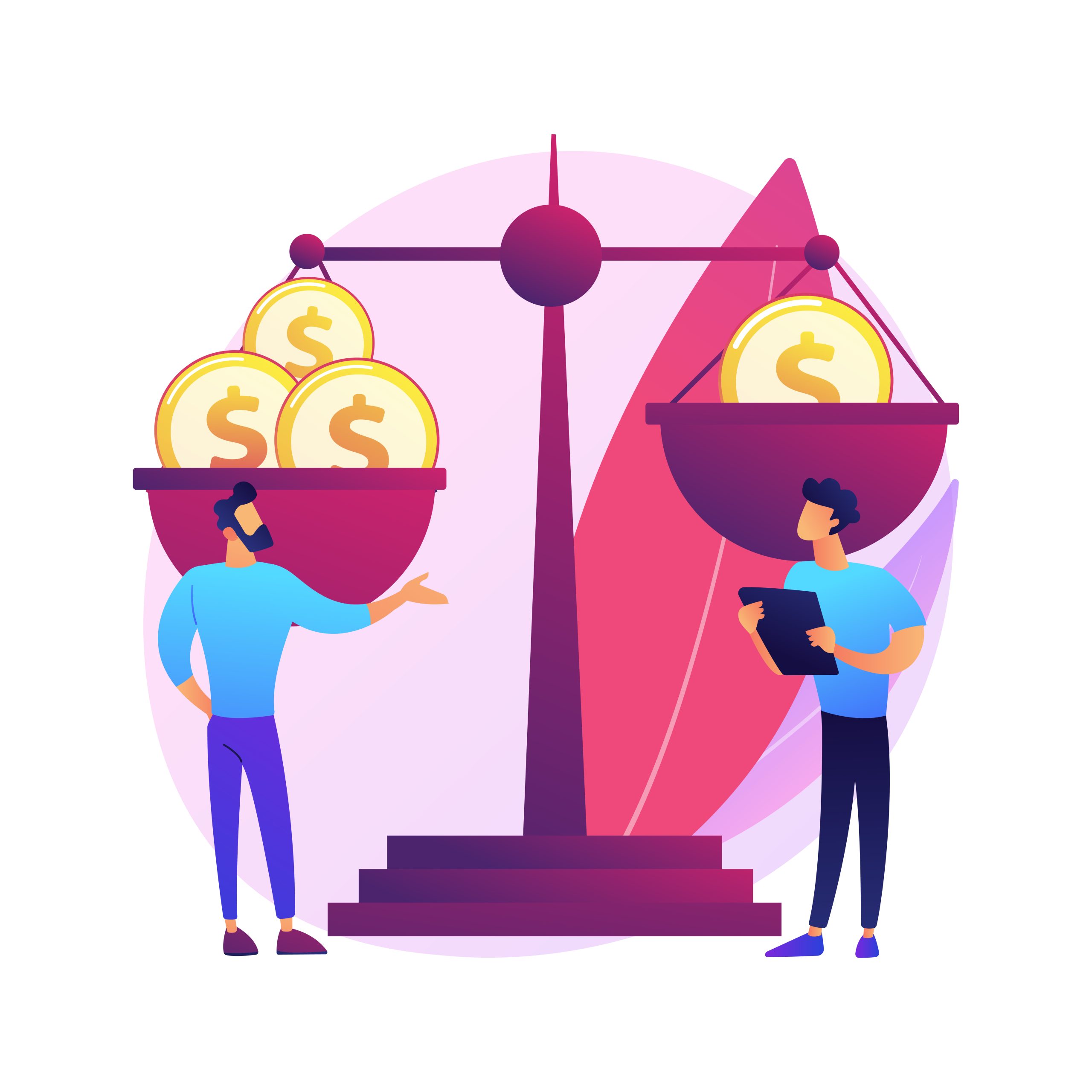
The accounting equation is a fundamental principle that provides insight into a company’s financial health. Students and professionals in finance and accounting need to understand how this equation works. Here, we’ll break down the concept and illustrate it with practical examples.
Breaking Down the Accounting Equation
1. Components of the Equation
- Assets: These include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and property. Assets are resources that a company owns and uses to generate income.
- Liabilities: These are obligations like loans, accounts payable, and mortgages. They represent what the company owes to others.
- Equity: This is the owner’s claim on the business assets, often referred to as net assets. It’s the residual interest in the assets after deducting liabilities.
2. The Fundamental Equation
The accounting equation is expressed as:
Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity
This equation is always in balance and forms the basis of a company’s balance sheet.
Application in Financial Transactions
1. Double-Entry Bookkeeping
Each financial transaction affects at least two accounts, maintaining the balance of the accounting equation. This is the core of double-entry bookkeeping.
2. Example Transactions
- Obtaining a Loan: A company taking a $10,000 loan increases its cash (Asset) and loan payable (Liability) by $10,000.
- Purchasing Equipment: Buying equipment for $5,000 cash decreases one asset (Cash) and increases another (Equipment) by $5,000.
Understanding Through Financial Statements
1. The Balance Sheet
The balance sheet directly reflects the accounting equation. It shows a snapshot of the company’s financial position, detailing assets, liabilities, and equity.
2. Income Statement and Equity
The income statement shows revenues and expenses over a period, affecting the equity portion of the equation. For example, earning $3,000 in revenue increases assets (Cash or Accounts Receivable) and equity (Retained Earnings) by $3,000.
Practical Examples
Real-Life Scenarios
- Sales on Credit: Making a sale of $2,000 on credit increases assets (Accounts Receivable) and equity (Revenue).
- Paying Rent: Paying $1,000 for rent decreases assets (Cash) and equity (through Expense).
A Balancing Act
The accounting equation is a balancing act that reveals a lot about a company’s financial status. Understanding this equation is crucial for step in understanding what accounting is about and analyzing a company’s financial statements and making informed decisions. As a student of accounting, familiarizing yourself with this concept and its practical applications is an essential step in your educational journey.
"Are you tired of struggling in accounting class? Let us make accounting easy and enjoyable for you."